Energy & Climate ~Mitigate Climate Change~
- Our Approach to Climate Change
- Targets and results
- Initiatives for Mitigating Climate Change
- Performance Data
- Examples of Initiatives for Mitigating Climate Change
- Case Study 1: A Sales Office with a full EV fleet using 100% electricity derived from locally-produced renewable energy
- Case Study 2: Model Store that Carries Out Energy Management for Electricity Generated via Renewable Energy Sources
- Case Study 3: Initiatives in Collaboration with Local Communities
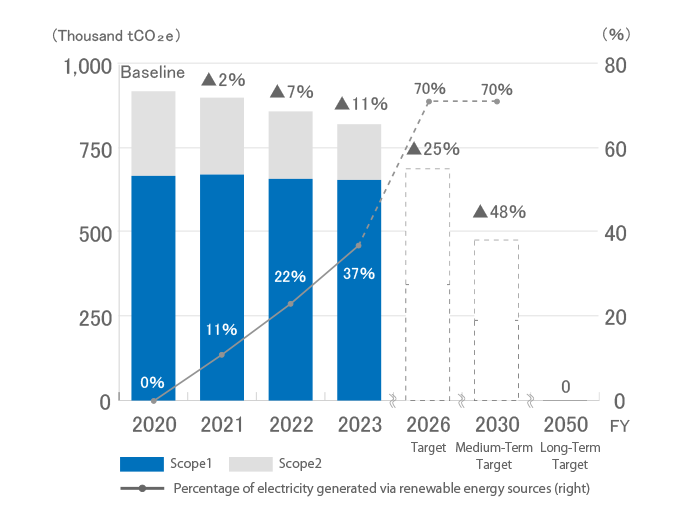
Climate change is one of the most important issues for the international community. The Yamato Group has identified "Energy & Climate" as one of its materialities and is strengthening initiatives to address climate change based on its environmental policy. Aiming to achieve virtually zero in-house greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2050 and a 48% reduction of in-house GHG emissions by 2030 (compared with fiscal 2020), we will promote initiatives to be achieved by 2030. These initiatives mainly consist of the introduction of 23,500 EVs, installation of 810 solar power generation units, creation of an operating structure that eliminates the use of dry ice, and an increase in the ratio of electricity use from renewable energy to 70%.
Our Approach to Climate Change
The Yamato Group recognizes that climate change is an important issue for creating a sustainable society, and for the Group itself. We identify and evaluate climate-related risks, opportunities, and impacts and strive to disclose information based on the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD*). The Group aims to contribute to the realization of a low-carbon society by mitigating and adapting to climate change through our business activities, managing risks and creating opportunities, and growing together with society.
- *The TCFD was established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) in 2015. In 2017, it issued recommendations on climate-related financial disclosures.
For information regarding disclosure in accordance with the recommendations of the TCFD, please refer to the Response to the Recommendations of the TCFD.
For information regarding disclosure in accordance with the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (TCFD), please refer to the Response to the Recommendations of the TCFD.
Targets and results
Medium- to Long-Term Target
Long-term target: Virtually zero in-house GHG emissions by 2050*
Medium-term target: Reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 48%* by 2030 (compared to fiscal 2020)
- *The company's own emissions (Scope 1 and Scope 2)
For details of our medium- to long-term targets, please refer to the news release “Realization of Reduction Targets for 2030 Aimed at Virtually Zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions by 2050” (Japanese Only).

Targets for each year
2024–2026 targets
2021–2023 targets
2023 target and results
| Materiality | FY2023 Targets | FY2023 Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy & Climate | |||||
| Mitigate Climate Change | Reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 10% compared to fiscal 2020*1 | GHG emissions were reduced 7% from fiscal 2020 | |||
| Reduce greenhouse gas emission intensity by 10% compared to fiscal 2020*1*2 | GHG emission intensity was reduced 6% compared to fiscal 2020 | ||||
| Use 40% of electricity generated via renewable energy sources*3 | Electricity generated via renewable energy sources accounts for 22% of total electricity used | ||||
| Reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 3% compared to 2022*4 | GHG emissions of consolidated subsidiaries overseas 3% reduction vs. fiscal 2022 | ||||
| Low-carbon transportation/offices: *Introduce low-carbontechnology *Enhance operational efficiency |
Continue field tests of new electric vehicles (EVs) and fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) (including medium size trucks for long-distance travel) with other industries | Started trial of FC large-size truck travel between Haneda Chrono Gate and Gunma Base | |||
| Carry out investigations and collaborative research into automated mobility*5 with the aim of realizing a low-carbon transportation and preventing air pollution | Continued discussions and confirmation of technology regarding automated mobility with business partners | ||||
| Reduce the use of dry ice to refrigerate packages: Substitute with 13,000 mechanical cold boxes and 1,200 refrigerator trucks |
Conducted supplementary procurement of cooling packs and adjusted the volume of coolant input Substituted 1,262 freight carrier trucks with refrigerator trucks |
||||
| Electric vehicles (EVs) 1,500 units | Introduced 1,754 Evs | ||||
| Visualize operational status and enhance transport efficiency based on data by fully leveraging digital technologies. Promote eco-driving | Increased the number of roll box pallets loaded per vehicle by 2.3 pallets compared to fiscal 2020 | ||||
| Promote modal shifts (180 units for rail and sea transports) |
Increased loading efficiency by consolidating bases and adjusting cargo sorting precision Annual number of inter-hub transport operations Reduced by 72,308 compared to fiscal 2020 |
||||
| Conduct demonstration tests of a model sales office that uses 100% renewable energy | Continued demonstration tests of a model Sales Office that uses 100% renewable energy | ||||
| Consolidate touch points (locations) and install LED lights | Consolidated touch points (locations) and installed LED lights at 411 locations | ||||
| Measure energy and optimize energy management | Reinforce energy management | Launched the development of a system to optimize EV operations, standardize charging, and implement flexible inter-base power distribution | |||
| Conduct financial analysis and promote low-carbon investment | Analyze scenario and reflect in financial planning (reflect in next medium-term plan) | Conducted additional financial analysis of physical risks for Yamato Transport in fiscal 2023, looking at the decrease in revenue due to flooding and damage to equipment and facilities | |||
| Put internal carbon pricing (ICP) into operation, confirm effects, and consider use as an investment indicator | Examined the scope of application for ICP and implementation methods | ||||
- Please use the scroll bar to see the rest of the table.
*1 In-house emissions of consolidated companies and Swan Co., Ltd. in Japan (Scope1 & Scope2).
*2 tCO2e /100 million yen of operating revenues.
*3 Consolidated companies and Swan Co., Ltd. in Japan.
*4 Overseas. Scope1 and Scope2.
*5 Automated mobility such as autonomous driving and truck platooning



For more targets, please refer to the Sustainable Strategies, Goals, and Results.
Initiatives for Mitigating Climate Change
Promotion of the Introduction of EVs and environmentally-friendly vehicles
In progressing the Yamato Group’s shift to low-carbon vehicles, we aim to introduce 23,500 electric vehicles (EVs) by 2030.
To date, we have been actively promoting the replacement of existing vehicles with environmentally-friendly ones that suit the necessary transportation method and distance.
As of the end of fiscal 2023, we had 2,275 EVs and 36,002 environmentally-friendly vehicles (LPG vehicles, CNG (natural gas) vehicles, hybrid vehicles), and 3,606 power-assisted vehicles. 84% of Yamato Transport’s pickup and delivery vehicles are environmentally-friendly.
We use electric power-assisted vehicles and hand-pushed trolleys for short-distance transportation in urban areas to reduce our GHG emissions.
We began the introduction of small-sized, commercial-use BEV trucks*1 for medium-distance transportation in August 2022. In September 2023, we launched the introduction of the first 2t truck EVs*2 at Yamato Transport. Further, in November 2023, we launched demonstrations for light EVs*3 utilizing removeable batteries within pickup and delivery operations. We can achieve more efficient energy management by utilizing removeable batteries that are charged with electricity generated via renewable energy sources, such as solar power, during daylight hours.
While reducing GHG emissions is difficult from a technical perspective*4 for long-distance transportation, we are striving to resolve issues. Yamato Transport launched demonstrations of large-sized, fuel-cell trucks together with suppliers and other companies*5 in May 2023.
As a transportation business, we have been able to support the shift to low-carbon technology not only within the Group but also society as a whole by utilizing transportation equipment that is highly energy efficient and utilizing vehicles with low GHG emissions.
- *1Hino Dutro Z EV developed by Hino Motors, Ltd.
- *2New eCanter small-sized electric truck developed by Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation
- *3Test vehicle MEV-VAN Concept developed by Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
- *4“Energy Technology Perspective 2020” published by the International Energy Agency
- *5Toyota Motor Corporation, Hino Motors, Ltd., Asahi Group Holdings, Ltd., NEXT Logistics Japan, and Seino Transportation Co., Ltd.
| Vehicle type | Key features | Introduction Status |
|---|---|---|
 Hino Motors |
・Super low floor and walkthrough type small BEV ・Easy to move from driver’s seat to cargo area,and get on/off vehicle ・Can be driven with ordinary license |
Introduced approx. 860 vehicles (as of Mar. 2024) |
 Mitsubishi Fuso |
・2-ton truck type EV ・Compact and easy to maneuver, despite its loading capacity ・Supports three temperature zones (room temperature, chilled and frozen) ・Cartridge type model is under development by the manufacturer |
Introduced approx. 900 vehicles (as of Mar. 2024) |
 Honda “MEV-VAN Concept” |
・Light commercial EV that uses replaceable batteries ・Will verify operations to reduce GHG emissions of Yamato and partner companies |
Start trials from Nov. 2023 |
 Progress of initiatives (FCV) |
・Large fuel cell truck which uses hydrogen as fuel ・Jointly developed by Toyota and Hino Motors ・Cruising range: approx. 600 km ・Since heavy-duty trucks are required to have sufficient cruising range, payload capacity, and the ability to refuel in a short time, the effectiveness of the fuel cell system using hydrogen, which has a high energy density, will be verified |
May 17, 2023 Start of trunk-route transportation trial (between Haneda Chronogate Base and Gunma Base) |
Use of Renewable Energy
The Yamato Group aims to increase the proportion of its electricity derived from renewable energy to 70% by 2030. In fiscal 2023, we purchased approx. 211,105 MWh of electricity derived from renewable energy sources, used approx. 1,263 MWh of electricity generated by our own solar power systems, and used approx. 1,994 MWh of electricity through PPAs*1. As a result, the percentage of electricity used that was derived from renewable energy sources increased from 21.8% in fiscal 2022, to 37.3% in fiscal 2023.*2
- *1PPA: Power Purchase Agreement
- *2The reporting boundary is consolidated companies in Japan and Swan Co., Ltd.



Introduction of Low-Carbon Technologies and Enhancement of Operational Efficiency
The Yamato Group actively introduces (procures) low-carbon technologies for use in transportation and at its business sites. An example is the compact mobile refrigerator *1we developed with a supplier. Using this refrigerator, we can reduce the amount of dry ice (CO2) used in the delivery of refrigerated and frozen goods. Additionally. we are changing to LED lighting and promoting energy saving at logistics warehouses. We are also working to increase transportation efficiency through modal shifts by making use of ferries*2 and railways, which offer better long-term transportation capability and lower environmental impact than trucks, through reducing inefficient services, and through joint transportation.
- *1D-mobico developed with Denso Corporation
- *2Launched a modal shift from July 2021 that utilizes marine transportation in collaboration with Tokyo Kyusyu Ferry Co., Ltd., which operates under the SHK Line Group



Increasing Low-Carbon Products and Services
The Yamato Group is expanding its range of low-carbon products and services that offer improved customer convenience, limit redeliveries and reduce GHG emissions. For details, please refer to “Provision of Environmentally Friendly Products and Services”.
Yamato Transport implemented a Carbon Neutrality Declaration for its three parcel delivery products: TA-Q-BIN, TA-Q-BIN Compact, and EAZY in January 2024. The declaration indicates that the company achieved carbon neutrality*1 compliant with the international standard ISO 14068-1:2023*2 in fiscal 2022 (April 2022–March 2023), and states the company’s commitment to realizing carbon neutrality for the three parcel delivery products by 2050 through continued ongoing initiatives to reduce its own GHG emissions associated with business activities. For fiscal 2022, the unabated emissions*3 has been offset*4 by retiring carbon credits*5 to achieve carbon neutrality.
The "Carbon Neutrality Report" was published on the corporate website of Yamato Holdings, showing the details of GHG emission reductions in fiscal 2022 and specific plans for maintaining carbon neutrality, including reduction, removal, and offsetting of GHG emissions until fiscal 2050. This claim was verified by BSI Group Japan K.K., a third-party organization, and Yamato Transport received an opinion statement regarding the carbon neutrality*1 of the three parcel delivery services in accordance with ISO 14068-1:2023.
For details of the declaration, please refer to “Carbon Neutral Delivery —TA-Q-BIN.”
- *1A status where GHG emissions are decreased and any remaining GHG emissions above zero are offset during a specified period
- *2An international standard specifying principles and requirements for achieving and verifying carbon neutrality
- *3GHG emission of the subject remaining after activities resulting in GHG emission reductions within the boundary of the subject
- *4Counterbalancing of the carbon footprint, by retiring a carbon credit(s)
- *5Tradeable certificate representing one tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent from GHG emission reductions or GHG removal enhancements

Collaboration with our business partners
The Yamato Group implements green logistics in collaboration with partners, such as joint transportation operations, contributing to improving transportation efficiency and reducing fuel consumption throughout the industry. For details, please refer to Green logistics in collaboration with our business partners.
Adaptating to Climate Change
The Yamato Group is reinforcing countermeasures for and increasing its resilience toward ever-worsening natural disasters. Please refer to Adaptation to Climate Change
Performance Data
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
In fiscal 2023, Yamato Group’s direct greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the use of fuel, etc. (scope 1), were approx. 656,732 tCO2, and indirect emissions associated with the purchase and use of electricity or heat (scope 2) were approx. 166,350 tCO2. Scope 1 emissions were 22% of the GHG emissions identified and scope 2 emissions were 5%. Scope 3 emissions, other indirect emissions, were approx. 2,218,292 tCO2, which was 73% of all emissions.
For detailed data regarding energy (including electricity derived from renewable energy sources) and GHG emissions, please refer to “Environmental data.”


- Boundary/Scope of coverage: Scope 1 and scope 2 GHG emissions of consolidated companies and Swan Co., Ltd. in Japan (emissions used to calculate total emissions and GHG emission intensity)
- Calculation methods and emission factor: Please refer to Calculation methods and conversion factors.
- Third-party guarantee covers the fiscal 2023 GHG emissions of Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd. Please refer to Environmental Data.
Scope3 * emissions (FY2023)
| Category | Emission volume (tCO2e) | Emission rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.Purchased Goods and services | 1,779,105 | 80 |
| 2.Capital goods | 186,390 | 8 |
| 3.Fuel and energy-related activities not included in Scope1 or Scope2 | 133,456 | 6 |
| 4.Upstream transportation, and distribution | N/A | - |
| 5.Waste generated in operations | 2,806 | 0 |
| 6.Business travel | 6,781 | 0 |
| 7.Employee commuting | 54,984 | 2 |
| 8.Upstream leased assets | N/A | - |
| Subtotal (upstream) | 2,163,523 | 98 |
| 9.Downstream transportation and distribution | N/A | - |
| 10.Processing of sold products | N/A | - |
| 11.Use of sold products | 54,741 | 2 |
| 12.End-of-life treatment of sold products | 28 | 0 |
| 13.Downstream leased assets | N/A | - |
| 14.Franchises | N/A | - |
| 15. Investments | N/A | - |
| Subtotal (downstream) | 54,768 | 2 |
| Total | 2,218,292 | 100 |
- Please use the scroll bar to see the rest of the table.
- Percentages of emissions in the table above are the percentage of scope 3 emissions.
- For information on data boundary and calculation methods, please refer to Calculation methods and conversion factors. Percentages of emissions in the table above are the percentage of scope 3 emissions.
*Scope 3 emissions are indirect emissions outside of scope 1 and 2 emissions.
Numbers of Environmentally-Friendly Vehicles, Including EVs
We are promoting a transition to low-carbon vehicles such as EVs. We had 2,275 EVs as of the end of fiscal 2023 and, going forward, we aim to introduce 23,500 EVs by 2030.
In addition, we have been using transportation methods with low environmental impact, such as environmentally-friendly vehicles, power-assisted bicycles, and carts. As of the end of fiscal 2023, we had 38,277 environmentally-friendly vehicles and 3,606 power-assisted bicycles, with environmentally-friendly vehicles making up 84% of Yamato Transport’s pickup and delivery vehicles.


Additional detailed energy and climate-related information can also be found in the Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd. CDP climate change questionnaire response.
Examples of Initiatives for Mitigating Climate Change
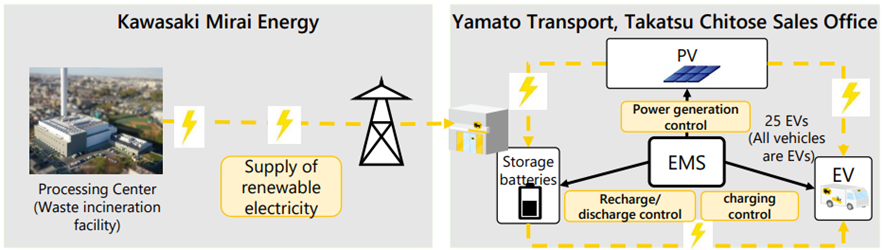
Case Study 1: A Sales Office with a full EV fleet using 100% electricity derived from locally-produced renewable energy
At the Takatsu Chitose Sales Office, in addition to the rooftop solar power generation equipment and storage batteries, renewable electricity supplied by KAWASAKI MIRAI Energy and generated within Kawasaki City is used to power the building and all 25 EVs used for pickup and delivery operations. Furthermore, Yamato Transport's proprietary energy management system (EMS) visualizes and automatically adjusts the amount of electricity used in the Sales Office, the amount of electricity generated by solar power equipment, and the amount of charge in storage batteries in real time to ensure efficient energy management.
Kawasaki City, KAWASAKI MIRAI Energy, and Yamato Transport jointly won the Climate Change Action Award from the Minister of the Environment for this initiative at the 2024 Climate Change Action Minister of the Environment Award, held by the Ministry of the Environment.
Case Study 2: Model Store that Carries Out Energy Management for Electricity Generated via Renewable Energy Sources
From September 2023, the Yawata Sales Office (Yawata City, Kyoto Prefecture) of Yamato Transport Co., Ltd. launched full-scale operations as a model store that carries out energy management for electricity generated via renewable energy sources.
The Yawata Sales Office is the first in Japan to operate with a full fleet of electric vehicles (EVs). By introducing solar power generation equipment and batteries, we generate electricity during the daytime to provide charging for EVs and a portion of the building’s electricity needs.* Furthermore, we are carrying out energy management, such as reducing the bias in peak electricity supply by simultaneously charging EVs at night through a system that standardizes electricity generation and other measures.
- *For the portion that cannot be covered by solar power generation, we purchase CO2-free electricity from KEPCO THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY CO., INC.



Case Study 3: Initiatives in Collaboration with Local Communities
In July 2022, Yamato Transport’s project to realize green delivery was selected as a project in the Green Innovation Fund Project/Smart Mobility Society Construction by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO). This project advances initiatives aimed at energy management through the introduction and operation of EVs within Gunma Prefecture. As of the end of fiscal 2023, we have introduced 50 EVs within Gunma Prefecture, and are gradually developing measures in each location.
In June 2023, Yamato Transport Co., Ltd. concluded a partnership agreement on co-creation for achieving carbon neutrality with Gunma Prefecture to further reinforce collaboration between the two parties with the aim of achieving carbon neutrality and a sustainable society that is beneficial to all citizens, companies, and local communities.


